- Zwischen 2011 und 2020 wurden im Referenzmarkt USA ein Rekordwert von 331 Mio. Fahrzeuge wegen sicherheitstechnischer Mängel zurückgerufen. Dies entspricht einer Rückrufquote von 201 Prozent, d.h. es wurden mehr als doppelt so viele Fahrzeuge zurückgerufen als im gleichen Zeitraum an Neuwagen verkauft wurden.
- Die Auswertungen der Rückrufe des Jahres 2020 und des 1. Halbjahres 2021 zeigen keine Trendumkehr, sondern verstärken den Negativtrend. Die Anzahl der zurückgerufenen Fahrzeuge der globalen Hersteller beläuft sich im Jahr 2020 auf 30,3 Mio. und im ersten Halbjahr 2021 bereits auf 18,6 Mio. Pkw. Die Rückrufquoten liegen mit 208 Prozent (2020) bzw. 227 Prozent (2021) damit wiederum über dem 10-Jahres Durchschnitt.
- Im Jahr 2020 mussten Toyota, Honda sowie der US-Hersteller Ford die meisten Fahrzeuge aufgrund von Sicherheitsmängeln in die Werkstätten beordern. Die höchsten Rückrufquoten verzeichneten neben Volvo insbesondere die japanischen Konzerne Honda, Mitsubishi und Toyota. In der ersten Hälfte des Jahres 2021 sind der Premium-Hersteller Daimler sowie die US-Konzerne General Motors und Ford besonders betroffen.
Rückruf-Trends der Automobilhersteller im Vergleich 2020 – 1. HJ 2021
Die Rückrufe der Automobilhersteller bewegen sich weiter auf sehr hohem Niveau. Nach aktuellen Berechnungen wurden auf dem Referenzmarkt USA im Gesamtjahr 2020 30,3 Mio. Pkw wegen sicherheitstechnischen Mängeln zurückgerufen. Im ersten Halbjahr 2021 waren es bereits über 18,6 Mio. Pkw (inkl. LCV). Damit liegt die Rückrufquote, die die Anzahl der zurückgerufenen Fahrzeuge an den Neuzulassungen des Jahres ausdrückt, mit 208 Prozent im Jahr 2020 (2019: 219%) bzw. mit 227 Prozent im ersten Halbjahr 2021 wiederum auf einem überdurchschnittlich hohen Niveau. Das sind die zentralen Ergebnisse der Studie „Rückruf-Trends der globalen Automobilhersteller 2011-2021“ des Center of Automotive Management (CAM) in Bergisch Gladbach, das die Rückrufe der OEMs jährlich bilanziert.
Mit Rückrufquoten jenseits von 400 Prozent schneiden im Jahr 2020 die Hersteller Volvo, Honda und Mitsubishi am schlechtesten ab. Toyota ruft mit einer Quote von 328 Prozent und rund 7 Mio. betroffener Fahrzeuge die meisten Pkw wegen sicherheitstechnischer Mängel in die Werkstätten zurück, gefolgt von Honda mit 5,8 Mio. Pkw sowie Ford mit rund 5 Mio. Fahrzeugen. Die geringsten Rückrufquoten besitzen im Jahr 2020 Tesla (13%), Mazda (26%), GM (53%) und Jaguar Land Rover (75%). Die deutschen Automobilhersteller BMW, Volkswagen und Daimler liegen mit jeweils 126, 121 und 86 Prozent eher im Mittelfeld.
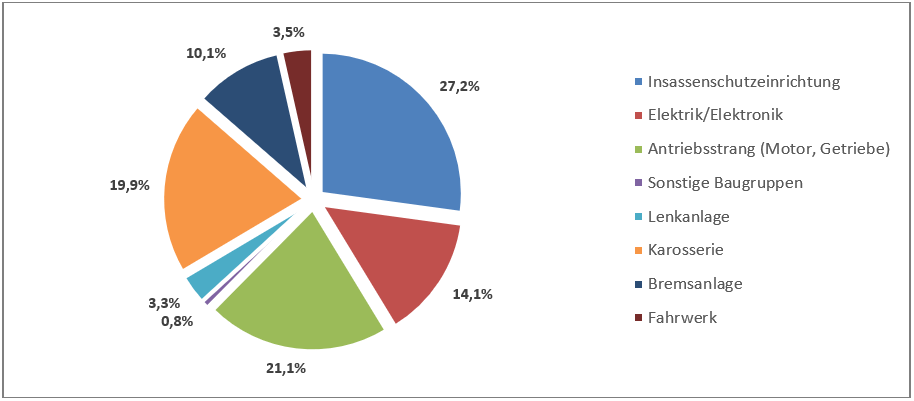
Rund 27 Prozent aller sicherheitsrelevanten Produktmängel im Jahr 2020 entfielen auf den Insassenschutz, während Qualitätsmängel beim Antriebsstrang (Motor, Getriebe) rund 21 Prozent der Rückrufe ausmachten. Auf die Karosserie zurückzuführende Sicherheitsmängel sind für rund 20 Prozent der zurückgerufenen Fahrzeuge verantwortlich, gefolgt von Problemen mit der Elektrik und Elektronik (14%) sowie Mängel an den Bremsanlagen (10%). Die erstmalige Auswertung von Rückrufen aufgrund von Softwarefehlern zeigt, dass deswegen im Jahr 2020 rund 7 Prozent der Pkw zurückgerufen werden mussten, was einem Volumen von knapp 2 Mio. Fahrzeugen entspricht. Die meisten Software-Probleme sind mit einem Anteil von 89 Prozent Honda zuzuordnen, gefolgt von Volvo mit 6 Prozent sowie Fiat-Chrysler mit knapp 2 Prozent.
Abbildung 1: Verteilung der sicherheitsrelevanten Mängel auf Baugruppen im US-Markt 2020
Im 1. Halbjahr 2021 liegt die Zahl der Rückrufe im US-Markt bereits bei 18,6 Mio. Pkw, was einer Rückrufquote von 227 Prozent entspricht. Eine hohe Rückrufmenge verbuchen dabei die amerikanischen Konzerne: der Marktführer GM kommt auf rund 7 Mio. Pkw, während Ford 3,7 Mio. Pkw zurückruft. Deren Rückrufquote liegt mit 525 bzw. 374 Prozent auf sehr hohem Niveau. Noch schlechter schneidet Daimler ab, die bei einem US-Absatz von rund 160.000 Pkw im ersten Halbjahr 2021 rund 2 Mio. Pkw zurückrufen müssen, was einer Rückrufquote von 1.275 Prozent entspricht. Mehr als die Hälfte aller sicherheitsrelevanten Produktmängel im 1. Halbjahr 2021 entfielen auf den Insassenschutz, während auf Elektrik/Elektronik 17,5 Prozent und auf den Antriebsstrang knapp 10 Prozent entfielen. Die übrigen Bereiche wie Fahrwerk (8%), Bremsanlage (6%), Karosserie (4%), Lenkanlage (2%) und sonstige Baugruppen (1%) nehmen eher eine untergeordnete Rolle ein. Mit einer absoluten Rückrufmenge von knapp 2,7 Mio. Fahrzeugen bzw. einem Anteil von rund 15 Prozent übersteigen Software-Mängel bereits zum Ende des Halbjahr 2021 den Gesamtjahreswert von 2020. Daimler musste mit einem Anteil von rund 64 Prozent die meisten Fahrzeuge aufgrund von Softwarefehlern zurückrufen, gefolgt von Subaru (17%), General Motors (11%) sowie Tesla (5%).
Im 1. Halbjahr 2021 liegt die Zahl der Rückrufe im US-Markt bereits bei 18,6 Mio. Pkw, was einer Rückrufquote von 227 Prozent entspricht. Eine hohe Rückrufmenge verbuchen dabei die amerikanischen Konzerne: der Marktführer GM kommt auf rund 7 Mio. Pkw, während Ford 3,7 Mio. Pkw zurückruft. Deren Rückrufquote liegt mit 525 bzw. 374 Prozent auf sehr hohem Niveau. Noch schlechter schneidet Daimler ab, die bei einem US-Absatz von rund 160.000 Pkw im ersten Halbjahr 2021 rund 2 Mio. Pkw zurückrufen müssen, was einer Rückrufquote von 1.275 Prozent entspricht. Mehr als die Hälfte aller sicherheitsrelevanten Produktmängel im 1. Halbjahr 2021 entfielen auf den Insassenschutz, während auf Elektrik/Elektronik 17,5 Prozent und auf den Antriebsstrang knapp 10 Prozent entfielen. Die übrigen Bereiche wie Fahrwerk (8%), Bremsanlage (6%), Karosserie (4%), Lenkanlage (2%) und sonstige Baugruppen (1%) nehmen eher eine untergeordnete Rolle ein. Mit einer absoluten Rückrufmenge von knapp 2,7 Mio. Fahrzeugen bzw. einem Anteil von rund 15 Prozent übersteigen Software-Mängel bereits zum Ende des Halbjahr 2021 den Gesamtjahreswert von 2020. Daimler musste mit einem Anteil von rund 64 Prozent die meisten Fahrzeuge aufgrund von Softwarefehlern zurückrufen, gefolgt von Subaru (17%), General Motors (11%) sowie Tesla (5%).
Für die insgesamt hohen Rückrufmengen und -quoten können im Einzelfall sehr unterschiedliche sicherheitsrelevante Bauteile verantwortlich sein:
- Toyota musste im Jahr 2020 insgesamt fast 2,9 Mio. Fahrzeuge der Modellreihen Avalon, Corolla und Matrix zurückrufen, weil die elektronische Kontrolleinheit des Airbags eine Fehlfunktion aufwies.
- Rund 2,1 Mio. Pkw verschiedener Modellreihen (u.a. Transit, Mustang, Fiesta) wurden vom US-Hersteller Ford zurückbeordert, weil eine bereits durchgeführte Reparatur an der Türverriegelung möglicherweise nicht ordnungsgemäß durchgeführt wurde. Zudem rief Ford 2021 bereits 2,6 Mio. Pkw der Typen Ranger, Fusion und Explorer zurück, weil die Frontairbags an der Fahrerseite unkontrolliert auslösen könnten, wenn sie längere Zeit einer hohen Luftfeuchtigkeit oder hohen Temperaturen ausgesetzt sind.
- Die größte Rückrufmenge im ersten Halbjahr 2021 verbuchte der US-Konzern General Motors. Insgesamt wurden bis Juni rund 4,4 Mio. Fahrzeuge (u.a. Cadillac Escalade) in die Werkstätten gerufen, weil die Gefahr bestand, dass die Airbags unkontrolliert auslösen könnten. Ende August 2021 gab General Motors zusätzlich bekannt, dass neuerdings alle produzierten Pkw des Typs Chevrolet Bolt EV aufgrund eines Risikos von Batteriebränden zurückgerufen werden. Die Umrüstungskosten der circa 140.000 betroffenen Fahrzeuge bezifferte der Hersteller auf rund eine Milliarde US-Dollar.
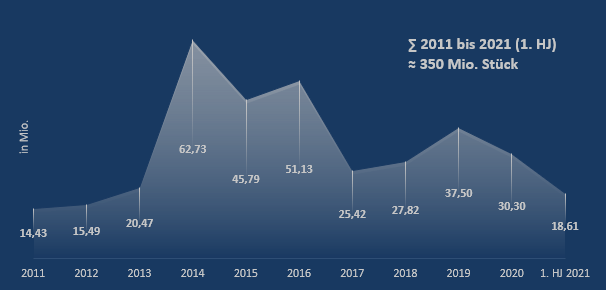
Abbildung 2: Sicherheitstechnische Rückrufe von Pkw/LCV im US-Markt 2011 – 2021 (1. HJ.) (in Mio.)
Hierzu Studienleiter Stefan Bratzel:
„Die hohen Rückrufzahlen der letzten Jahre sind auch Kennzeichen des enormen Veränderungsdrucks, der auf der Branche lastet. Insgesamt ist bereits abzusehen, dass Probleme rund um das Batteriesystem sowie Softwareprobleme erheblich zunehmen werden. Allerdings stellen sicherheitstechnischen Rückrufe nur die Spitze des Eisbergs dar. Nicht selten gleicht die Produktherstellung mancher Automobilunternehmen einer „Bananenentwicklung“: Das Produkt reift erst beim Kunden. Das verärgert vielfach die Autokäufer und kann zu Personen- und Sachschäden führen. Außerdem kostet es die Hersteller mittel- und langfristig viel Geld und schadet ihrem Image.“
Rückrufe im Langzeitvergleich
In den letzten 10 Jahren (2011–2020) wurde ein Allzeit-Negativrekord von über 331 Mio.(!) zurückgerufenen Fahrzeugen allein im Referenzmarkt USA erreicht, was einer durchschnittlichen Rückrufquote von 201 Prozent entspricht. Inklusive des 1. Halbjahrs 2021 wurden seit dem Jahr 2011 349,7 Mio. Pkw zurückgerufen (Rückrufquote von 204%). D.h. es wurden mehr als doppelt so viele Fahrzeuge in die Werkstätten zurückbeordert als im gleichen Zeitraum an Neuwagen verkauft werden konnten (vgl. Abbildung 2). Ein Großteil der betroffenen zurückgerufenen Modelle bezieht sich entsprechend auf weiter zurückliegende Baujahre.
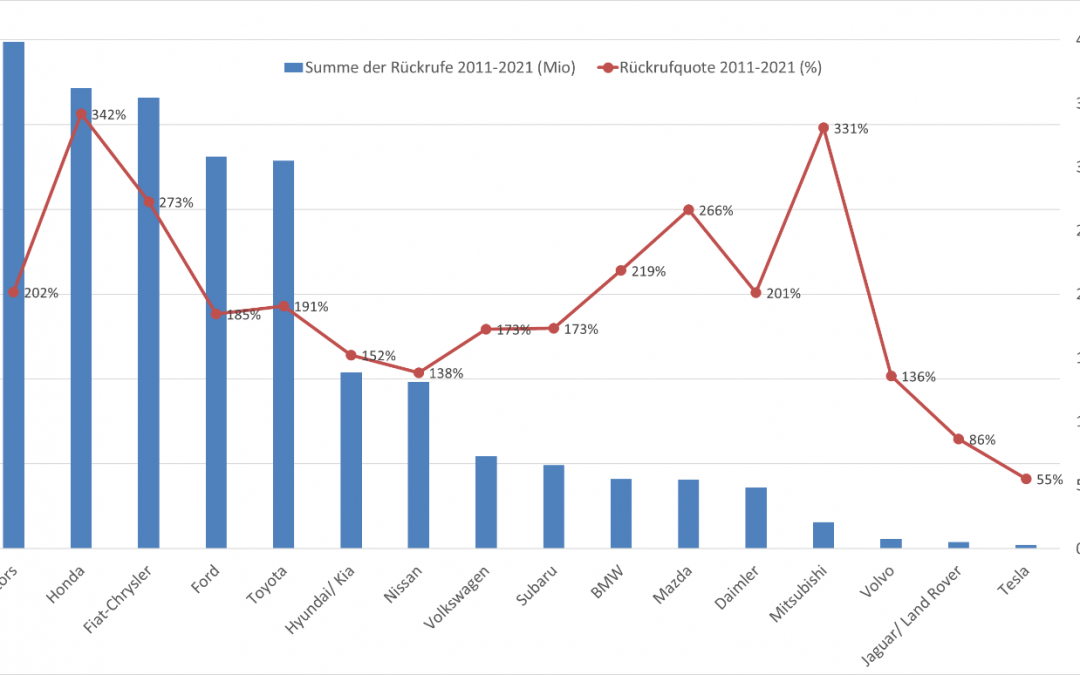
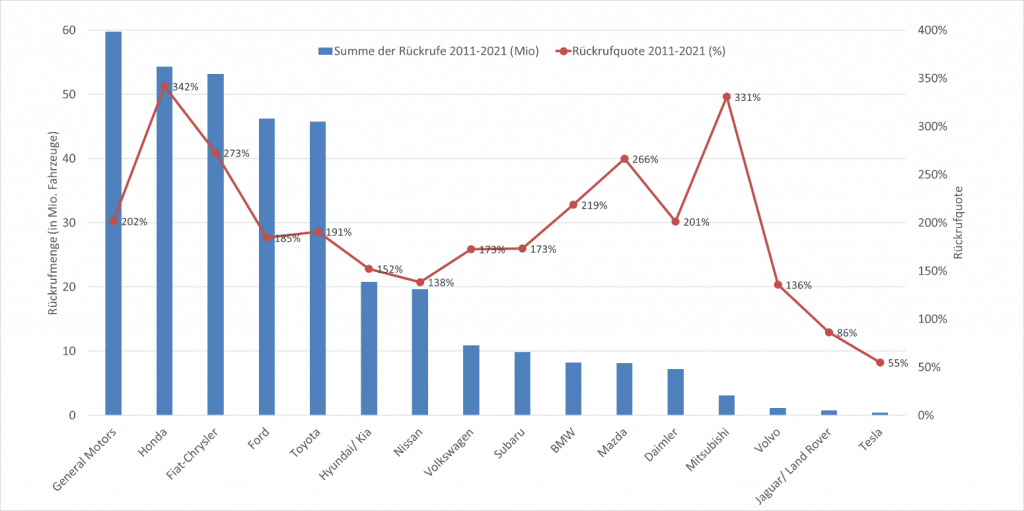
Nach Herstellern sind General Motors, Honda, Fiat-Chrysler sowie Ford und Toyota besonders betroffen, die binnen einer Dekade zwischen 60 und 46 Mio. Pkw wegen Sicherheitsmängeln zurückrufen mussten (vgl. Abbildung 3). Mit 342 Prozent erreicht Honda auch den Negativ-Spitzenwert bei der Rückrufquote vor Mitsubishi (331%), Fiat-Chrysler (273%) und Mazda (266%). General Motors, Toyota und Ford befinden sich mit Rückrufquoten zwischen 202, 191 und 185 Prozent im Mittelfeld. Überdurchschnittlich betroffen ist im Langzeitvergleich der Premiumhersteller BMW, der auf eine Rückrufquote von 219 Prozent kommt, während Daimler und der Volkswagen Konzern mit 201 bzw. 173 Prozent leicht unter dem Schnitt der betrachteten Hersteller liegen. Im Langzeitvergleich weisen Jaguar-Land Rover und Tesla mit 86 bzw. 55 Prozent die niedrigsten sicherheitsbezogenen Rückrufquoten der Branche auf gefolgt von Volvo (136%), Nissan (138%) und Hyundai (152%).
Abbildung 3: Rückrufmenge und Rückrufquoten der Pkw-Hersteller 2011-2021 (1.HJ) im US-Markt
Gründe für Qualitätsprobleme und Folgerungen
Die Rückrufe in den Jahren 2020 und 2021 (1. HJ) zeigen wiederum, dass die Produktqualität ein zentrales Thema in der Automobilindustrie bleibt. Wachsende Rückrufrisiken und steigende globale Sensibilität für Qualitätsmängel erfordern einen Paradigmenwechsel im Qualitätsmanagement der Automobilhersteller. Das Risiko großer Rückrufaktionen ist durch marken- und modellübergreifende Plattform- und Gleichteilestrategien sowie globale Produktionsnetzwerke erheblich gestiegen. Gleichzeitig werden sicherheitsrelevante Mängel an Fahrzeugen in den wichtigen Automobilmärkten immer weniger akzeptiert, gerade auch weil Kunden über länderübergreifende Internet-Blogs und Newsgroups sehr gut informiert sind. Sicherheitsrelevante Mängel können zu Todesfällen und Verletzungen der Autofahrer führen und darüber hinaus den Herstellern Imageverluste und hohe Kosten verursachen.
Das Qualitätsmanagement vieler Automobilhersteller trägt vielfach noch nicht den neuen globalen Produktsicherheitsanforderungen Rechnung. Manche Hersteller und Zulieferer betreiben zur kurzfristigen Gewinnmaximierung eher reaktive Qualitätsmanagementsysteme mit nachsorgender Mängelbeseitigung, teilweise unter billigender Inkaufnahme von Unfällen wie im Fall der Airbagmängel. Vor dem Hintergrund veränderter Entwicklungs- und Produktionsbedingungen und neuen Technologien und Funktionen im Fahrzeug sind jedoch proaktive und vorsorgende Produktqualitätsstrategien notwendig, bei denen umfassende und langfristige Kosten-/ Nutzenbetrachtungen im Mittelpunkt stehen müssen.
Hierzu Stefan Bratzel:
„Das Qualitätsmanagement der Hersteller muss vor dem Hintergrund neuer technischer Anforderungen sowie einer wachsenden Sensibilität der Öffentlichkeit eine deutlich höhere Relevanz in Automobilunternehmen erlangen. So entsteht etwa künftig neuer Kundennutzen durch Elektromobilität, Vernetzung und (teil-)autonome Fahrfunktionen. Aber es steigen dadurch auch in erheblichem Maße die Risiken. Die Cyber-Security von Fahrzeugen wird insgesamt zum großen Sicherheits- und Qualitätsthema der Branche aufsteigen, das wesentlich über die Akzeptanz von neuen Wachstumsfeldern der Automobilindustrie entscheidet. Abhilfe können Over-the-Air-Updates der Fahrzeugfunktionen schaffen, da viele Probleme durch softwaretechnische Optimierungen behoben werden können, ohne dass das Fahrzeug physisch in die Werkstatt muss. Derzeit beherrschen dies jedoch nur wenige Automobilhersteller.“
Zur Studie: Die Rückruf-Trends der globalen Automobilhersteller im Jahr 2020 und 2021 (1.HJ.) (AutomotivePERFORMANCE Report 2021)
Das Center of Automotive Management (CAM) analysiert seit dem Jahr 2005 jährlich die Rückrufe der globalen Automobilhersteller. Als Referenzmarkt wird dabei die USA gewählt. Der US-Markt ist aufgrund seiner Absatzgröße, der relativ scharfen Sicherheitsrichtlinien und vor allem des hohen Klagerisikos ein aussagekräftiger Indikator für die Produktqualität der Automobilkonzerne. Ein Rückruf wird von der National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in den USA registriert, wenn ein sicherheitsrelevanter Defekt an einem Fahrzeug auftritt oder das Fahrzeug bzw. dessen Teile nicht den Sicherheitsstandards entsprechen. Auslöser von Rückrufen sind häufig Beschwerden und Informationen zu Fahrzeugmängeln, z.B. von Autofahrern, die der NHTSA angezeigt werden. Kommt ein Hersteller seiner Anzeigepflicht nicht nach oder verzögert er einen Rückruf drohen hohe Strafen sowie Klagen in Millionenhöhe. Die Rückruf-Trends geben Hinweise darauf, dass die Produktqualität – gerade auch im Hinblick auf sicherheitsrelevante Merkmale im Fahrzeug – ein kritisches Thema der Branche bleibt, das nicht nur zu einer enormen direkten Kostenbelastung führen, sondern auch das Image von Fahrzeugherstellern enorm belasten kann.
Strukturelle Ursachen für wachsende Qualitätsprobleme.
1. Steigende technische Komplexität des Fahrzeugs
Die technische Komplexität der Fahrzeuge ist in den letzten 20 Jahren enorm gestiegen, wodurch die Fahrzeuge zwar grundsätzlich sicherer geworden sind. Allerdings führte die technische Komplexität auch zu einem Anstieg der Fehlerhäufigkeit und Fehleranfälligkeit. Hierzu tragen u.a. passive und aktive Sicherheitssysteme (wie ABS, ESP, Airbags; Fahrassistenzsysteme) bei, die gleichzeitig die Fahrzeugsicherheit deutlich erhöht haben. Darüber hinaus sind motortechnische Optimierungen (Start/Stopp-Systeme, Aufladung etc.) sowie zahlreiche Komfortmerkmale wie etwa Navigations- und Internetdienste im Fahrzeug zu nennen. Es ist zu erwarten, dass im Zuge der Entwicklung weiterer Komfort- und Sicherheitsfeatures sowie von Vernetzung und Softwarefunktionen auch künftig der Komplexitätsgrad der Fahrzeuge weiter deutlich zunimmt.
2. Zunahme der Entwicklungsgeschwindigkeit aufgrund gestiegener Wettbewerbsintensität
Die Produktentwicklungszyklen wurden in den vergangenen 15 Jahren deutlich verkürzt. Aufgrund der hohen Wettbewerbsintensität der Branche bringen die globalen Hersteller in immer kürzerer Zeit neue Modelle bzw. Derivate in Umlauf und verbreitern damit ihr Produktportfolio kontinuierlich. Wer es schafft mit neuen Modellen bzw. -varianten schnell am Markt zu sein, hat im globalen Wettbewerb Vorteile. Der hohe Zeitdruck in der Produktentwicklung wirkt sich negativ auf die Qualitätssicherung aus.
3. Wertschöpfungsverlagerung und Globalisierung der Entwicklung und Produktion
Um Kosten-, Zeit- und Innovationsvorteile zu realisieren, wurden erhebliche Teile der Wertschöpfung auf die Automobilzulieferer übertragen. Ihr Wertschöpfungsanteil ist mittlerweile auf rund 75 Prozent gestiegen. Gleichzeitig steigen mit dieser Verlagerung die Anforderungen an unternehmensübergreifendes Qualitätsmanagement, das darüber hinaus auf globaler Ebene sichergestellt werden muss. Es muss einerseits nicht nur die eigene Produktqualität, sondern auch durch geeignete Prozesse die Teilequalität der globalen Lieferanten gesichert werden. Andererseits steigt die Komplexität eines Qualitätsmanagements auch dadurch, dass die Automobilhersteller nicht nur die zugelieferten Teile, sondern meist auch die Qualität der international verteilten Produktionsanlagen ihrer Zulieferer einschätzen und durch Prozesse absichern müssen.
4. Erhöhter Kostendruck als Gefahr für Produktqualität
Die Automobilhersteller stehen aufgrund der hohen Innovations- und Wettbewerbsintensität auch unter enormen Kostendruck. Gleichzeitig geben die Hersteller den Kostendruck an die Automobilzulieferer weiter, die dazu angehalten sind ihre eigenen Kosten bzw. die ihrer Teile- bzw. Rohstofflieferanten zu drücken. Hier besteht die Gefahr, dass der Kostendruck zu Ungunsten der Teile- bzw. Produktqualität geht.
5. Baukasten- und Gleichteilestrategie
Um Kosten zu sparen und die Entwicklungsgeschwindigkeit zu erhöhen, müssen die Hersteller zunehmend auf Gleichteile- bzw. Baukastenstrategien setzen. Hierbei nutzen die OEM die gleichen Komponenten und Module in möglichst vielen Modellen, um von den hiermit verbundenen Mengeneffekten zu profitieren. Dadurch kann ein spät entdeckter Fehler im einem Baukastenmodul zu millionenfachen Fahrzeugrückrufen führen.